BRAUN, T., & DIERKES, P. (2017)
Connecting students to nature – how intensity of nature experience and student age influence the success of outdoor education programs.
Environmental Education Research 23(7): 937-949. https://doi.org/10.1080/13504622.2016.121486
Artikel auf Deutsch dazu: https://www.opel-zoo.de/files_db/1587543644_2666__8.pdf (Seiten 6/7).
Abstract:
Nature connectedness counts as a crucial predictor of pro-environmental behavior. For counteracting today's environmental issues a successful re-connection of individuals to nature is necessary. Besides the promotion of knowledge transfer the aim of the educational program presented in this study is to connect students to their environment. This research explores the impact of an outdoor environmental education program on primary and secondary school students' nature connectedness with regard to the extent of their nature experience and participant age. The intervention was implemented in two durations: one-day and five-days. Participants were divided into four subsamples from seven up to 18 years of age. Findings suggest that both intervention types evoke immediate shifts towards a stronger nature connectedness among students (p < 0.001). Notably, the five-day outdoor education interventions were significantly more effective in sustainably promoting nature connectedness compared to one-day field trips (p < 0.001). Seven to nine year old students performed the strongest shifts towards nature. The value of short-term and residential outdoor environmental education interventions is discussed.
braun-biblio
KLEESPIES, M. W., ALVAREZ MONTES, N., BAMBACH, A. M., GRICAR, E., WENZEL, V. & DIERKES, P. W. (2021)
Identifying factors influencing attitudes towards species conservation – a transnational study in the context of zoos.
Environmental Education Research 27(10): 1421-1439. https://doi.org/10.1080/13504622.2021.1927993
Abstract:
In the past decades, zoos have increasingly developed into conservation and education centers and today make an important contribution to environmental education. In this context, this study investigated which factors influence attitudes towards species conservation. The variables examined were gender, age, the number of visits to zoos in the last 12 months, perception of zoos, interest in animals and the country where the survey was conducted. A total of 3347 participants in seven different countries were surveyed. In the hierarchical multiple regression, it was found that all the variables examined were significant influencing factors with exception of gender. A mediator analysis provided evidence that the number of visits to zoos, in addition to the direct effect on attitudes towards species conservation, also has a relevant indirect effect with interest in animals as mediators. Significant differences in attitudes towards species conservation were found between some of the countries studied, but only with a small effect sizes.
kleespies-biblio
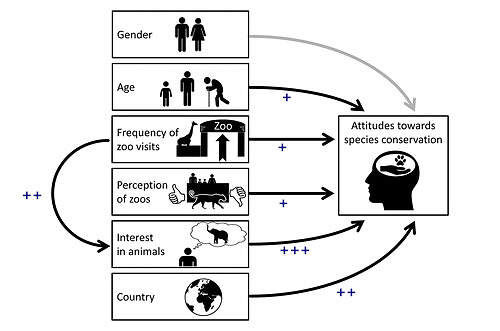
Faktoren, welche das Interesse an Tieren und die Haltung gegenüber dem Artenschutz beeinflussen
KÖGLER, J., BARBOSA PACHECO, I. & DIERKES P. W. (2020)
Evaluating the quantitative and qualitative contribution of zoos and aquaria to peer-reviewed science.
Journal of Zoo and Aquarium Research 2/2020: 124–132.
Abstract:
The EU Council Directive relating to the keeping of wild animals in zoos, as well as major global and regional zoo associations, calls upon zoos and aquaria to support biodiversity conservation and research. However, assessments of the scientific contribution of zoos remain scarce to date. This paper, therefore, evaluates for the first time the quantitative research productivity of the 71 members of the Association of Zoological Gardens (Verband der Zoologischen Gärten, VdZ) and analyses aspects of its qualitative outcome. Between 2008 and 2018, VdZ members produced or contributed to 1,058 peer-reviewed and mostly ISI Web of Science (WoS)-listed publications, with productivity rates increasing over time. They did so either as (co-)authors or by supporting external research teams with access to animals, data or biological samples deriving from their respective ex-situ animal collections. The publications resulted in 8,991 citations appearing in 284 mostly not zoo-related journals. These findings, plus the large range of subject areas and animal species focused on, suggest a broad audience group reached. It is concluded that VdZ member zoos and aquaria make valuable contributions in certain fields of peer-reviewed science of which benefits might accrue for evidence-based ex-situ and in-situ conservation planning and management.
kögler-biblio